这篇讲解 集合映射之List映射
1.通常对于集合,在hibernate中的处理都是使用set来完成。但是hibernate也提供了对于其他几种集合的映射。
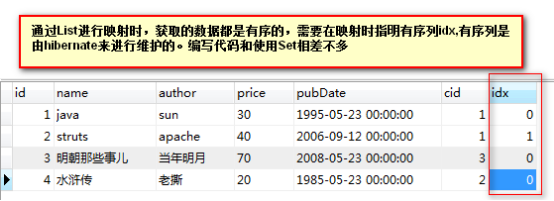
在这里实现List的映射,List是有序的集合,所以需要在表中有一列数据用来表示顺序。
2.集合映射一般存在于一对多中,使用案例是 category 和 book
3.类结构
Book.java
public class Book implements Serializable{ private int id; private String name; private String author; private double price; private Date pubDate; public Book() { } public Book(String name, String author, double price, Date pubDate) { super(); this.name = name; this.author = author; this.price = price; this.pubDate = pubDate; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getAuthor() { return author; } public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } public Date getPubDate() { return pubDate; } public void setPubDate(Date pubDate) { this.pubDate = pubDate; } @Override public String toString() { return "Book [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", author=" + author + ", price=" + price + ", pubDate=" + pubDate + "]"; }} Category.java
public class Category implements Serializable{ private int id; private String name; private List books = new ArrayList<>(); public Category() { } public Category(String name) { super(); this.name = name; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public List getBooks() { return books; } public void setBooks(List books) { this.books = books; }} 4.映射文件
Book.hbm.xml
Category.hbm.xml
5.测试
public class HibernateTest { /** * 生成数据库表的工具方法 * */ @Test public void testCreateDB(){ Configuration cfg = new Configuration().configure(); SchemaExport se = new SchemaExport(cfg); //第一个参数 是否打印sql脚本 //第二个参数 是否将脚本导出到数据库中执行 se.create(true, true); } /** * 初始化表数据 * 使用一对多的方式来保存数据,会执行update语句来更新外键 * 使得效率会比多对一的方式效率低 */ @Test public void testInit(){ Session session = null; Transaction tx = null; try { session = HibernateUtil.getSession(); tx = session.beginTransaction(); Category c1 = new Category("计算机类"); Category c2 = new Category("文学"); Category c3 = new Category("历史"); SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"); Book b1 = new Book("java","sun",30,df.parse("1995-05-23")); Book b2 = new Book("struts","apache",40,df.parse("2006-09-12")); Book b3 = new Book("明朝那些事儿","当年明月",70,df.parse("2008-05-23")); Book b4 = new Book("水浒传","老撕",20,df.parse("1985-05-23")); //设置关系 c1.getBooks().add(b1); c1.getBooks().add(b2); c2.getBooks().add(b4); c3.getBooks().add(b3); session.save(c1); session.save(c2); session.save(c3); session.save(b1); session.save(b2); session.save(b3); session.save(b4); tx.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { if(tx!=null) tx.rollback(); }finally { HibernateUtil.close(); } } /** * 在查询多的一端数据时可以获取一的一端的数据 */ @Test public void testGetData(){ Session session = HibernateUtil.getSession(); Category c1 = (Category)session.get(Category.class, 1); System.out.println(c1.getId()+"----"+c1.getName()); System.out.println("-----------------"); for(Book book:c1.getBooks()){ System.out.println(book); } HibernateUtil.close(); }}